Article
Vlf Converter
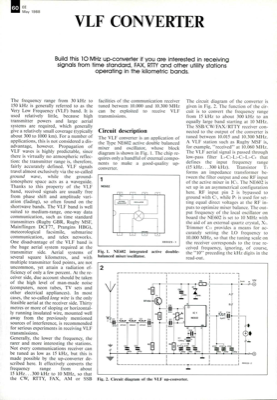
60 EE May 1988 The frequency range from 30 kHz to 150 kHz is generally referred to as the Very Low Frequency (VLF) band. It is used relatively little, because high transmitter powers and large aerial systems are required, which generally give a relatively small coverage (typically about 300 to 1000 km). For a number of applications, this is not considered a dis- advantage, however. Propagation of VLF waves is highly predictable, since there is virtually no atmospheric reflec- tion: the transmitter range is, therefore, fairly accurately defined. VLF signals travel almost exclusively via the so-called ground wave, while the ground- ionosphere space acts as a waveguide. Thanks to this property of the VLF band, received signals are usually free from phase shift and amplitude vari- ation (fading), so often found on the shortwave bands. The VLF band is well suited to medium-range, one-way data communication, such as time standard transmitters (Rugby GBR, Rugby MSF, Mainflingen DCF77, Pr...


Discussion (0 comments)